- Step-by-Step Input Guide
- Step 1: Input the power rating (Pmax, STC) [W]
- Step 2: Enter the max power voltage
- Step 3: Fill in the temperature coefficient Voc
- Step 4: Fill in the temperature coefficient Vmp
- Step 5: Type in the circuit voltage
- Step 6: Input the minimum temperature
- Step 7: Put the maximum temperature
- Step 8: Enter string length
- Step 9: Click calculate to proceed
- Step 10: Cross check results
Step-by-Step Input Guide #
To create a new calculation using our Voc calculator, enter the following parameters:
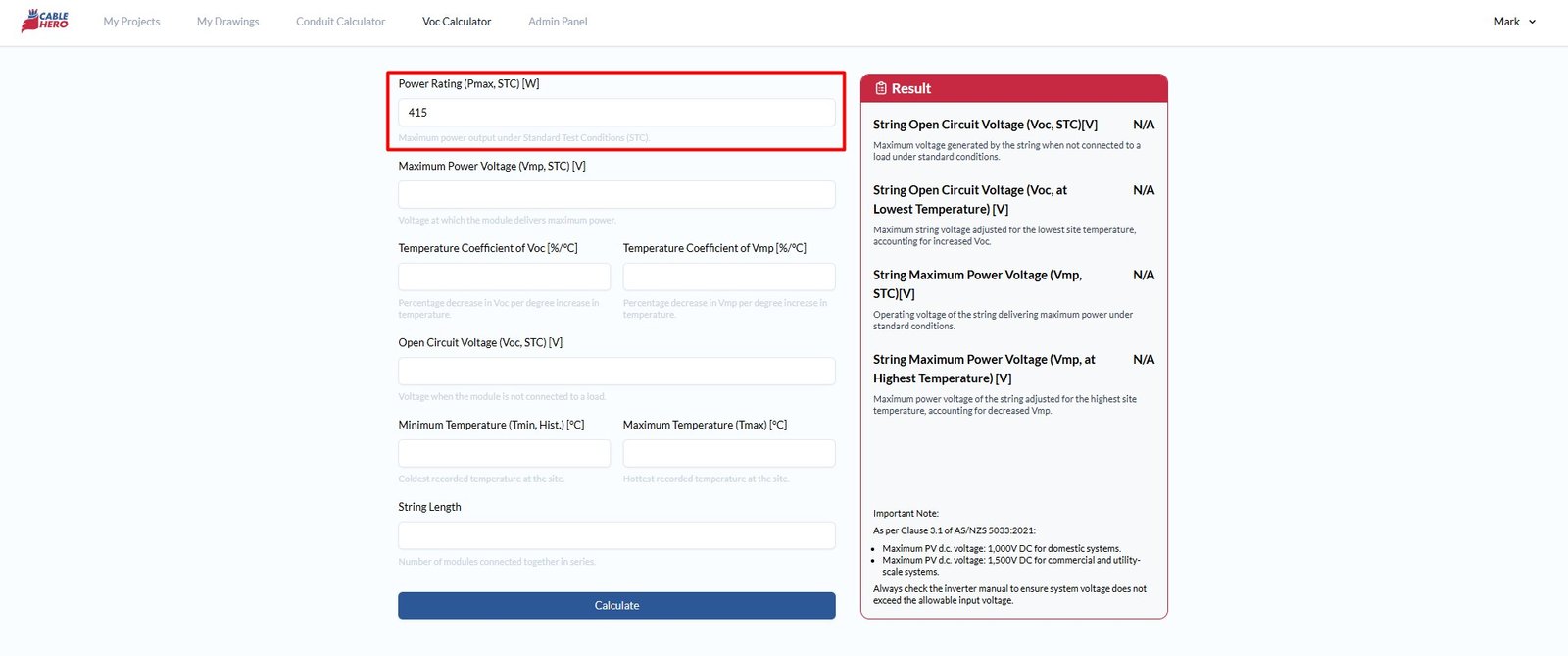
Step 1: Input the power rating (Pmax, STC) [W] #
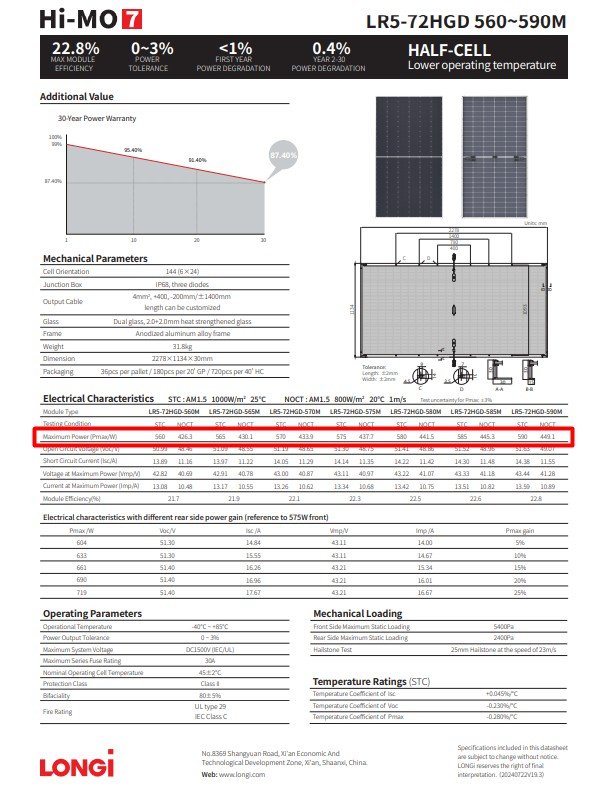
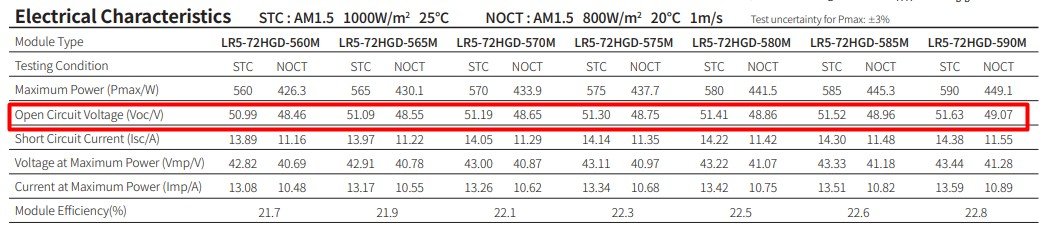
First, enter the information, which refers to the module’s rated maximum power output under Standard Test Conditions (STC). This value—commonly labeled as “Maximum Power” or “Pmax”—can be found on the PV module’s datasheet.
For user guidance, this datasheet is provided below with the Pmax value clearly highlighted to help you locate this parameter easily.
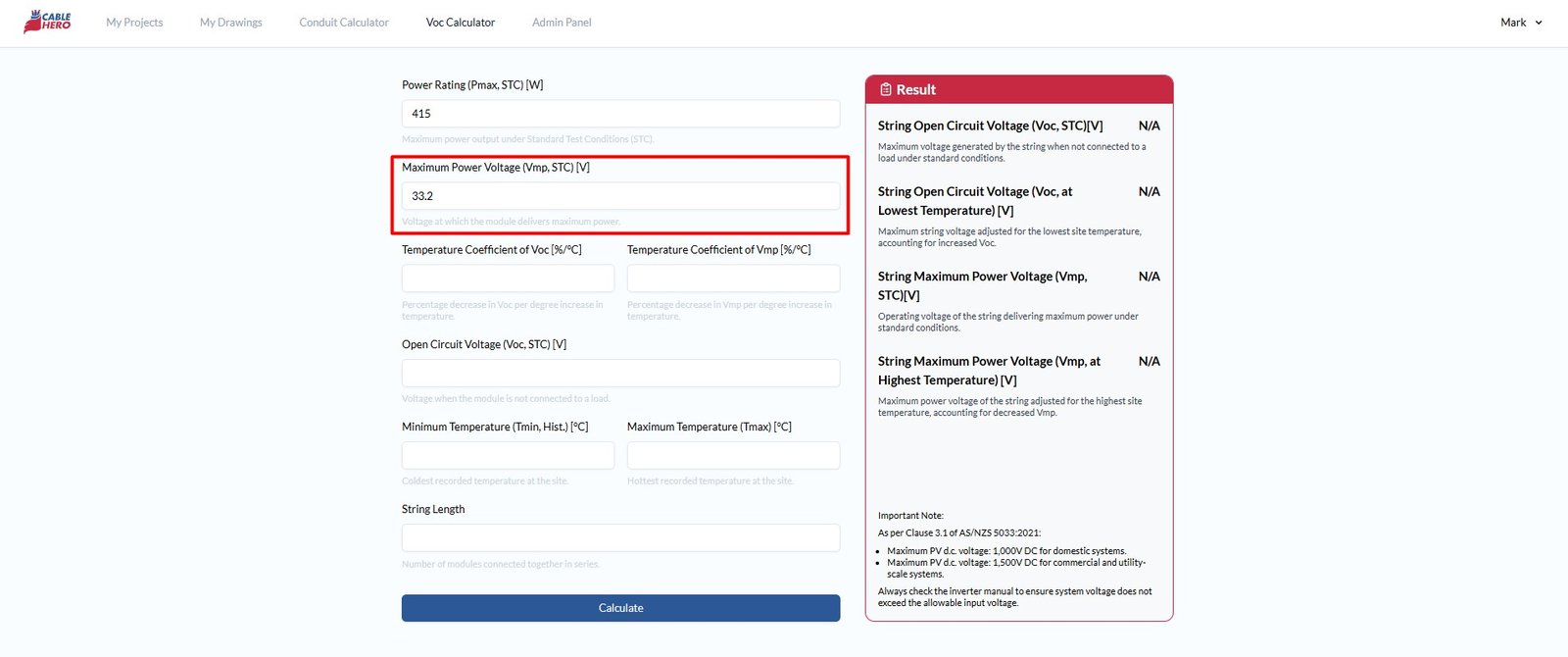
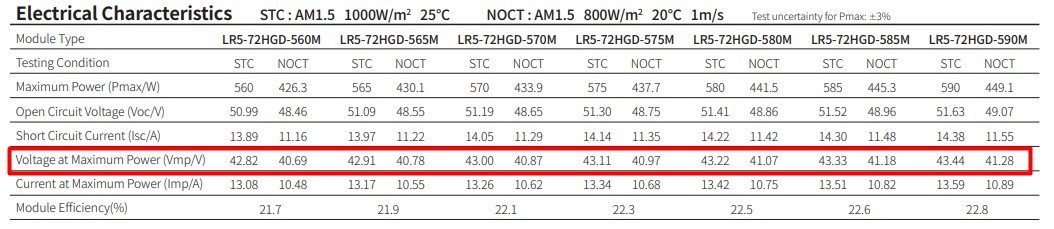
Step 2: Enter the max power voltage #
Next, type in the maximum power voltage (Vmp, STC) [V]. This is the voltage output when the module delivers at maximum peak power.
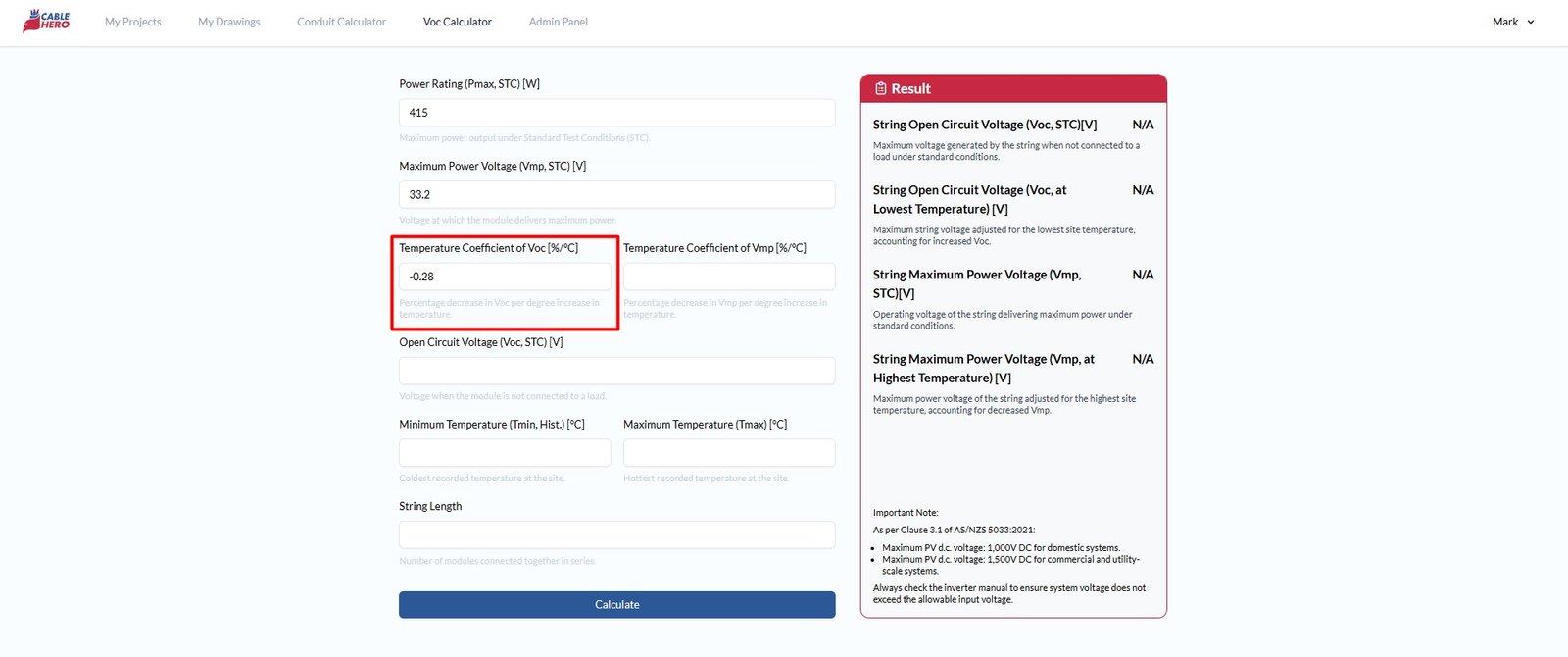
Step 3: Fill in the temperature coefficient Voc #
For the temperature coefficient of Voc [%/°C], simply rate of voltage change per °C for Voc. Do note that percentage decrease in Voc per degree increase in temperature.
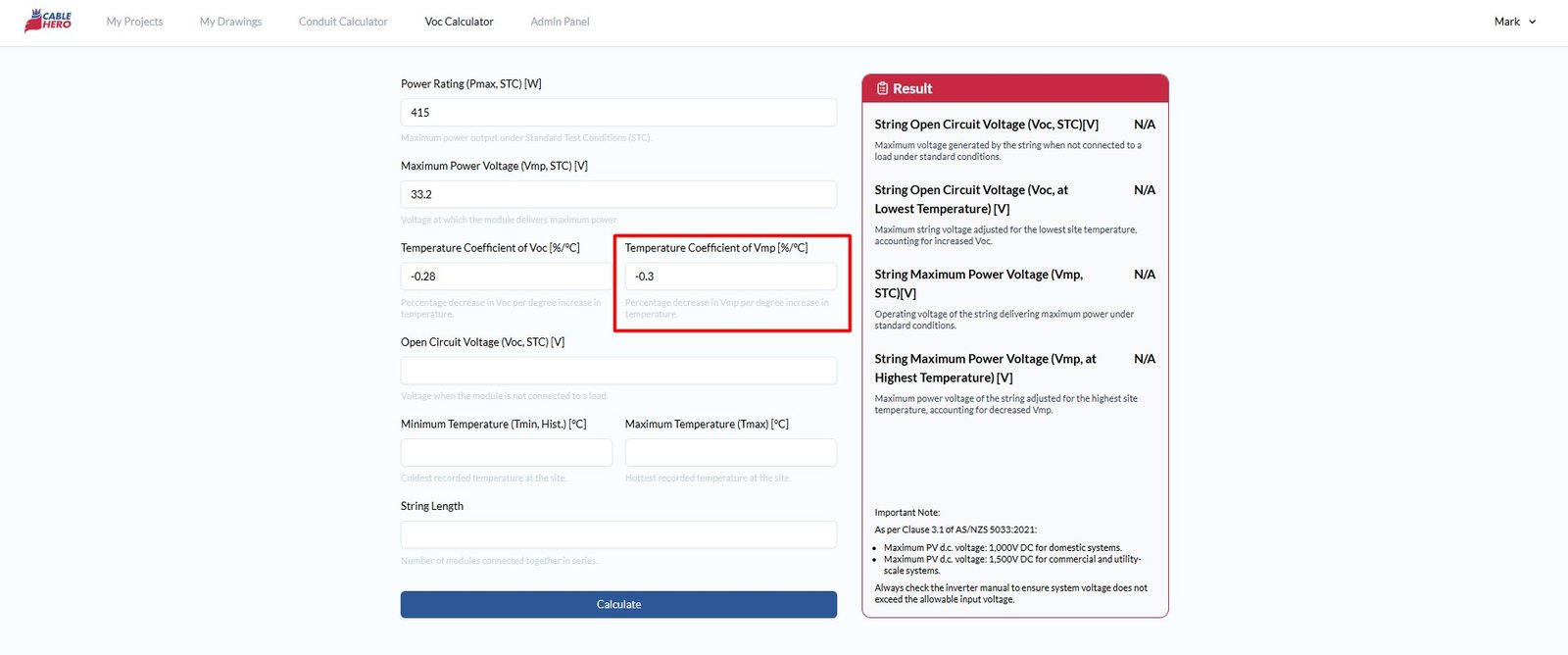
Step 4: Fill in the temperature coefficient Vmp #
Similar to Voc, the Vmp typically decreases as temperature increases. In this way, you need to input the temperature coefficient of Vmp to calculate adjusted voltage under varying thermal conditions.
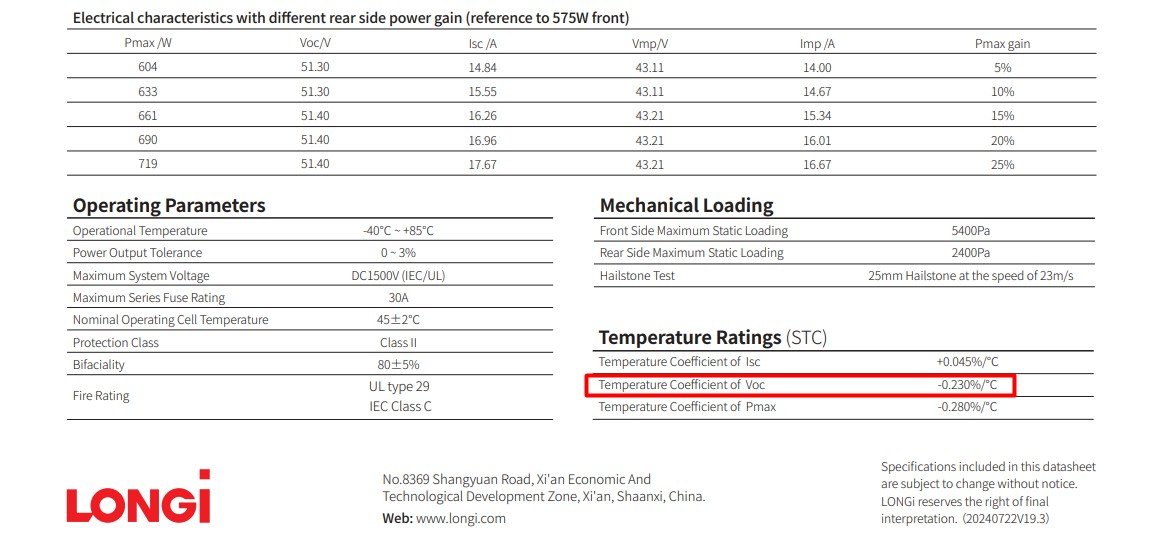
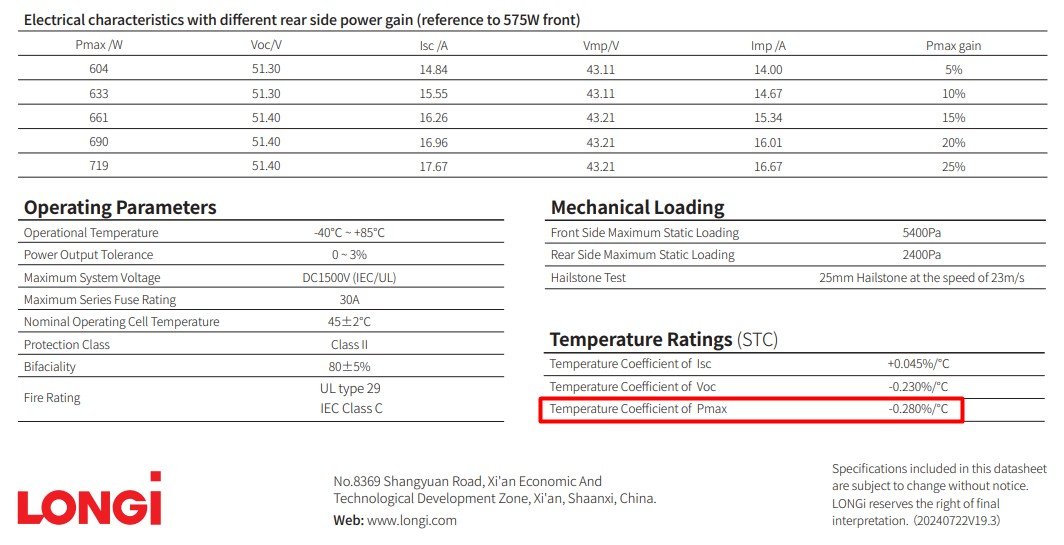
Note: Not all PV module datasheets provide a specific value for the Vmp temperature coefficient. In such cases, it’s reasonable to assume the same value as the temperature coefficient of Pmax, as they are often closely related in behaviour.
Step 5: Type in the circuit voltage #
When it comes to the open circuit voltage (Voc, STC) [V], input the voltage with no load applied under STC.
Step 6: Input the minimum temperature #
Type in your minimum site temperature (Tmin, Hist.) [°C] next as it identifies the lowest recorded temperature at the installation site.
Step 7: Put the maximum temperature #
To identify the highest recorded temperature at the installation site, you need to put the maximum site temperature (Tmax) [°C].
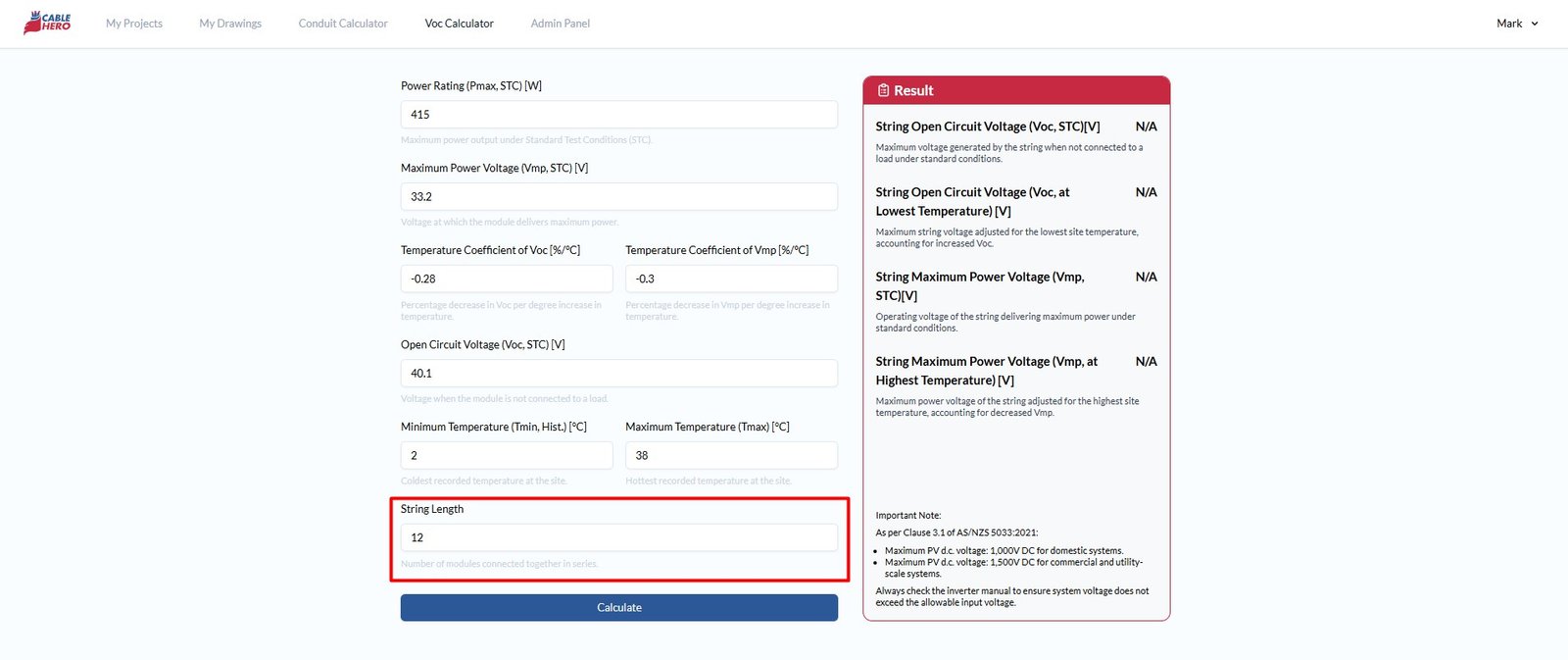
Step 8: Enter string length #
Lastly, type in the number of modules connected in series for the string length.
Step 9: Click calculate to proceed #
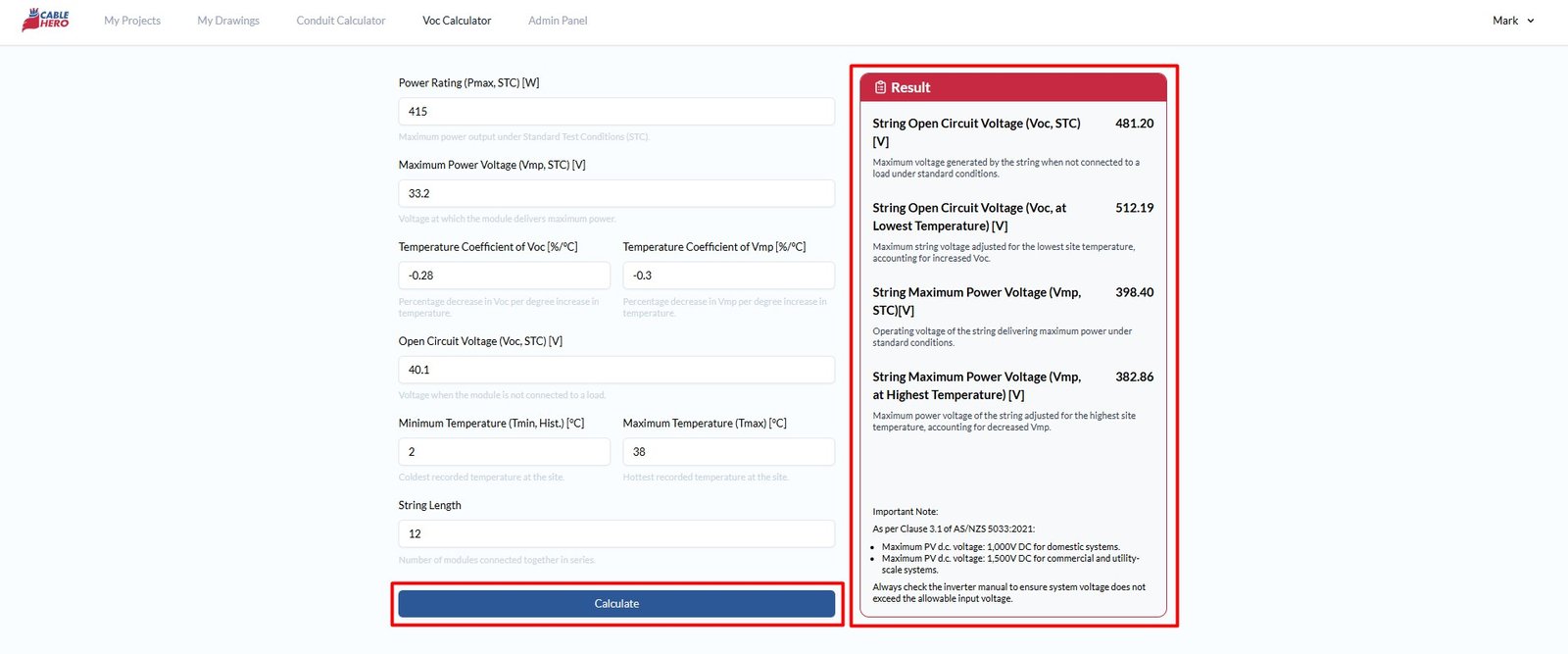
Once all fields are filled, click Calculate and CableHero will automatically compute the temperature-adjusted Voc based on the coldest site temperature and temperature-adjusted Vmp based on the hottest site temperature.
Each result provides critical design insight:
- String Open Circuit Voltage (Voc, STC)[V] – Maximum voltage generated by the string when not connected to a load under standard conditions.
- String Open Circuit Voltage (Voc, at Lowest Temperature) [V] – Maximum string voltage adjusted for the lowest site temperature, accounting for increased Voc.
- String Maximum Power Voltage (Vmp, STC)[V] – Operating voltage of the string delivering maximum power under standard conditions.
- String Maximum Power Voltage (Vmp, at Highest Temperature) [V] – Maximum power voltage of the string adjusted for the highest site temperature, accounting for decreased Vmp.
Step 10: Cross check results #
Ensure that adjusted Voc does not exceed the inverter’s maximum input voltage: 1,000V DC for domestic systems and 1,500V DC for commercial and utility-scale systems. Always cross-check results from our against inverter specifications.